Categories
Money money money...
Could we help you? Please click the banners. We are young and desperately need the money



Last updated: September 10th 2021
Categories: IT Knowledge
Author: Elzan Ajdari
RAID system explained



RAID
What is RAID?
RAID is a data storage technology that allows multiple hard drives to be combined into one storage space. There are several types of RAID, each offering different performance, storage capacity and reliability.
RAID 0
For RAID 0 you’ll need two hard drives at least. The data is distributed over several hard disks, if one of the hard disks gets lost, all the data is going to get lost. So, RAID 0 offers no security or speed for your data.
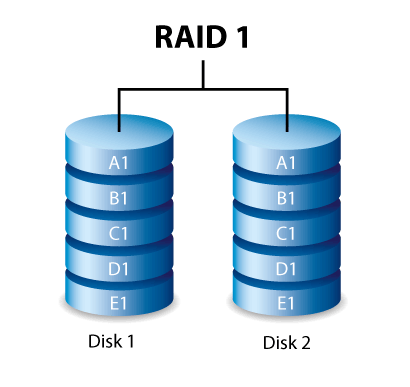
RAID 1
For RAID 1 you’ll also need two or more hard drives at least. The data is stored on multiple hard drives, so if one gets lost, the data is still available. But there is also a disadvantage. you need twice the number of hard disks because the effective storage capacity is halved. The used capacity of the available drives is therefore 50%.
RAID 5
For a RAID 5 you need at least 3 hard disks. The data is distributed on several hard drives. If a hard disk should fail, the RAID controller can use this parity to calculate the missing data. Although this procedure requires one hard disk less than an appropriate RAID 1 system, a parity value must be calculated for all data, which requires more computing power. A RAID 5 system can consist of a maximum of 16 hard disks.
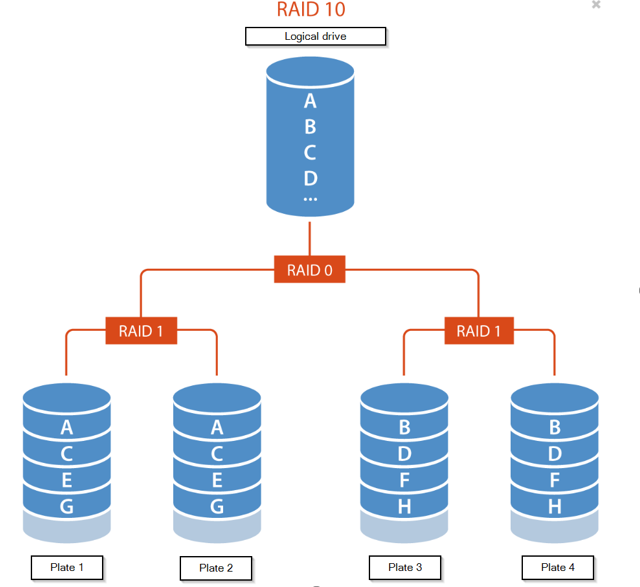
RAID 10
As the name says RAID 10 is basically the RAID 1 and RAID 0 together. For an RAID 10 you'll need 4 hard disks. The data will be halved and stored in the hard disks. So that is the same function like RAID 0. And the data will be mirrored and saved, like RAID 1. So your data is now secured and fast.